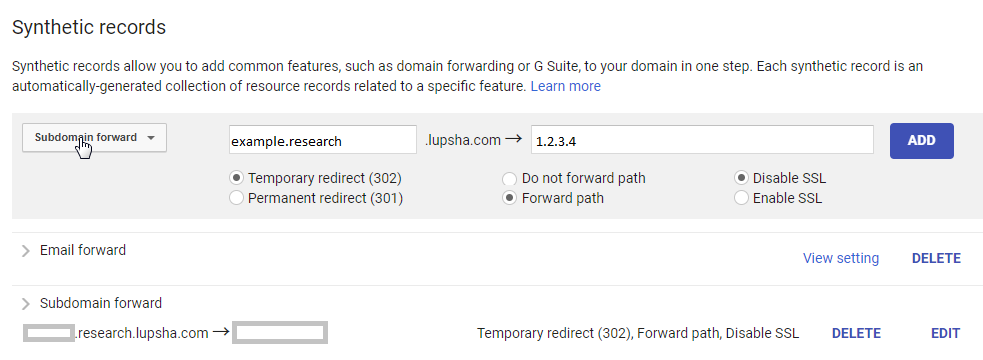
Set up the subdomain forward, and wait for it to propagate. When you can ping the domain, it’s ready.
Be root
sudo suEdit config file that’s available.
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/server.research.example.com
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80 ipv6only=on;
# listen 443 ssl;
# listen [::]:443;
# ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/server.research.example.com/fullchain.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.research.example.com/privkey.pem;
# include /etc/nginx/snippets/ssl.conf;
root /opt/web/server.research.example.com;
index index.html index.htm;
server_name server.research.example.com;
}
# force 80 to go to 443 SSL
#server {
# listen 80;
# server_name server.research.example.com;
# return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
#}Link it from available to enabled:
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/server.research.example.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/server.research.example.com
ls -la /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/server.research.example.comCreate empty dir to serve subdomain:
mkdir /opt/web
mkdir /opt/web/server.research.example.com
echo "example" > /opt/web/server.research.example.com/index.html
Restart nginx
/etc/init.d/nginx restartMake sure you can hit the URL over http (https not quite yet)
http://server.research.example.com (You might have to wait for the subdomain forward to work, refresh after waiting an hour – see step 1 above).
Once hitting the URL over http works, move on to creating certificates.
Install certbot
sudo apt-get install certbot python-certbot-nginxCreate new certificate
certbot --nginx certonly -d "server.research.example.com"Edit the config and comment/uncomment lines:
server {
# listen 80;
# listen [::]:80 ipv6only=on;
listen 443 ssl;
listen [::]:443;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/server.research.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/server.research.example.com/privkey.pem;
include /etc/nginx/snippets/ssl.conf;
root /opt/web/server.research.example.com;
index index.html index.htm;
server_name server.research.example.com;
}
# force 80 to go to 443 SSL
server {
listen 80;
server_name server.research.example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}And in this example I’m also using /etc/nginx/snippets/ssl.conf which you might not have, and it looks like:
nano /etc/nginx/snippets/ssl.conf
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers ECDH+AESGCM:ECDH+AES256:ECDH+AES128:DH+3DES:!ADH:!AECDH:!MD5;
ssl_ecdh_curve secp384r1;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 valid=300s;
resolver_timeout 5s;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15768000; includeSubdomains; preload";
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;Restart nginx
/etc/init.d/nginx restartTest by going to http, and it should take you automatically to https
http://server.research.example.com